Introduction to AWS databases¶
Source: Introduction to AWS databases

I recently got certified as an ‘AWS Cloud Practitioner’, during my learning journey services that got my attention the most were the vast variety of databases provided by AWS. As an ETL developer, I know how much selecting database type is important, because selecting or configuring a database in-correctly can cause severe repercussions.
AWS provides a vast variety of databases, with each one having unique features which are suitable for a wide range of applications. In this article, we are going to explore the tip of this iceberg. I know many of you, including me, have very little or no experience when it comes to AWS, so I guess this blog will help you to understand AWS better and also will give you a proper start for your journey into the cloud.
AWS focuses on modernizing infrastructure by providing purpose-built and fully managed databases. By fully managed means a database with storage, data, and compute services that are managed and maintained by a third-party provider instead of by an organization’s IT, staff. This provides benefits like high availability, reduced maintenance, and low operation cost.
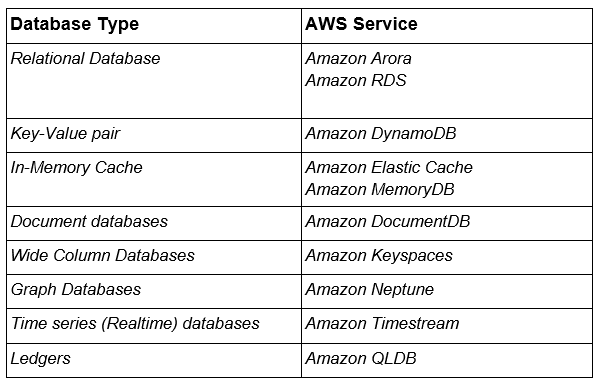
Here’s the snippet of all the types of databases provided by the AWS :
Amazon Aurora:
Amazon Aurora is a relational database built on the cloud, when we talk about relational databases first thing that come into our mind is that traditional enterprise database, these databases provided performance and availability to the enterprise, but the operational cost goes on increasing exponentially as enterprise tries to expand. So, what AWS did with Amazon Aurora, is that they combined the performance and availability of the enterprise databases with simplicity and cost-effectiveness of open-source databases. This gave rise to the MySQL and PostgreSQL-compatible relational databases known as Amazon Aurora.
What makes Amazon Aurora so unique, Aurora is five times faster than traditional MySQL databases and three times faster than PostgreSQL. As I mentioned before maintaining on-premises/enterprise databases was not the much money friendly, Aurora cost 1/10th of any commercial databases. The most attractive feature of Amazon Aurora is that it is a ‘Fully managed database’ which means, it automates time-consuming administration tasks like hardware provisioning, database setup, patching, and backups.
The main use of Amazon Aurora is for any enterprise application that can use a relational database. Any SaaS (Software as a Service) application requires a great deal of flexibility in instance and storage scaling along with high performance and reliability, which is provided by Amazon Aurora with a 90% cost reduction.
Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS):
So by name we know this will be a relational database, But before discussing this AWS service, I would like to point out how traditional systems work, before setting up your Relational Database, you need to provision hardware and perform all initial setups, you also need to synchronize your database with the other platforms, and once this is done, you need to perform administrative tasks and also perform patching and backup of the database. But after that, if you need to increase or decrease the capacity of your system then you need to perform all these tasks again. So, such traditional systems are not very cost and time-effective, making them almost obsolete in today’s ad-hoc world. The reason why Amazon RDS is the solution to these problems as it provides resizable data storage capacity which makes it cost-effective, and also it automated all the administrative tasks giving you time to focus more on the application.
Amazon RDS provides six familiar database engines:
MySQL, PostgreSQL, MariaDB, OracleDB, SQL Server, and AWS Aurora
In short Amazon, RDS is a managed SQL database service that facilitates the deployment and maintenance of relational databases in the cloud.
Amazon RDS is useful in applications where constant updates take place and which also require high availability. Some examples are Online retail stores, Streaming, or financial applications.
Amazon DynamoDB:
DynamoDB is totally different database system as compared to the two we discussed above. The first two systems were relational or SQL database systems, But DynamoDB is a no-SQL database service as it stores its data in the form of key-value pairs. Amazon DynamoDB is a fully managed serverless system built for high-performance operations. By high performance, it means that it is specifically built for the internet-scale global applications which can support petabytes of data and tens of millions of reads and write requests per second. As it’s a serverless system, there are no servers to provision, patch, or storage, so software to install, maintain or operate.
DynamoDB is adjust itself as per the need that means it can scale up or scale down automatically as the data demands, which makes it very cost-effective and scalable.
DynamoDB is used in IoT applications as it can store continuously incoming streams of data from sensors, another powerful use case for DynamoDB is in the gaming industry.
Amazon Elastic Cache:
Services we discussed up till this point were database systems, whereas Elastic Cache as the name suggests is a Caching system. It is a fully managed service. Elastic Cache finds itself useful in applications, like updating and managing gaming leaderboards, conducting real-time analysis of customers on e-commerce sites, and processing and relaying messages on instant messaging platforms.
Amazon Keyspaces:
Before starting with Keyspaces, we need to understand what Apache Cassandra is, Apache Cassandra is a highly scalable and highly available NoSQL distributed database. Amazon Keyspaces is managed Apache Cassandra compatible database service, Basically, with Amazon Keyspaces, you can run your Cassandra workload on AWS using Cassandra application codes. Keyspaces is mostly useful for high-speed applications that require very small latency, for example, trade monitoring.
Amazon DocumentDB:
DocumentDB is a fully managed document database service provided by AWS. It is mainly focused on JSON workloads and is MongoDB compatible. It is highly durable and provides a great range of scalability. It can support millions of read requests per second, which makes it a suitable option for mission-critical MongoDB workloads as you can use existing drivers and tools.
Amazon Neptune:
Amazon Neptune is a scalable high-performance graph database. In a relational database relationship between two tables is computed through a time-expensive JOIN query. Whereas graph database stores connections alongside the data in the model so with only a pattern and a set of starting points, graph databases explore the neighboring data around those initial starting points — collecting and aggregating information from millions of nodes and relationships — and leaving any data outside the search perimeter untouched. What amazon Neptune does, is provide a simple process for developers to write queries that can search connected data points with low latency. Neptune is useful in search engines, network security, fraud detection, and building knowledge graphs.
Amazon QLDB:
QLDB stands for Quantum Ledger Database, and it is a fully managed ledger database. With the rising of blockchain, businesses are trying to incorporate blockchain technology in day-to-day activities. So, AWS came with QLDB, which offers key features of a blockchain ledger system like immutability and transparency. We can’t say QLDB is a distributed system, but it is more of a distributed ledger technology with a centralized approach. Amazon QLDB finds itself useful in supply chain management as it can record any transaction so tracing any shipment becomes very easy if something goes wrong. QLDB is also helpful in the banking sector as it can store critical banking data like account transactions.
These are just a few of the services that AWS provides for data management. I know it is a lot to take in one article, But I have tried to simplify it as much as possible. If you find something that would make this blog more simplified or more interesting, please leave a comment I will surely try it in my next blogs. I hope this blog would have excited you to start the journey into the cloud.
Appendix: Links¶
-[[Obsidian Web Clipper Bookmarklet]] -[[3-Resources/Clippings/_README|Clippings]]